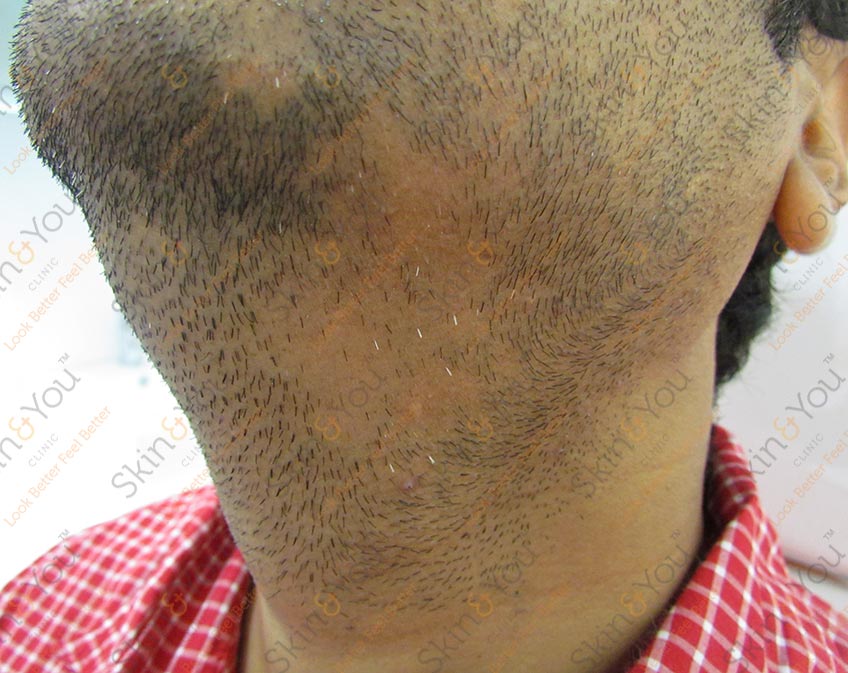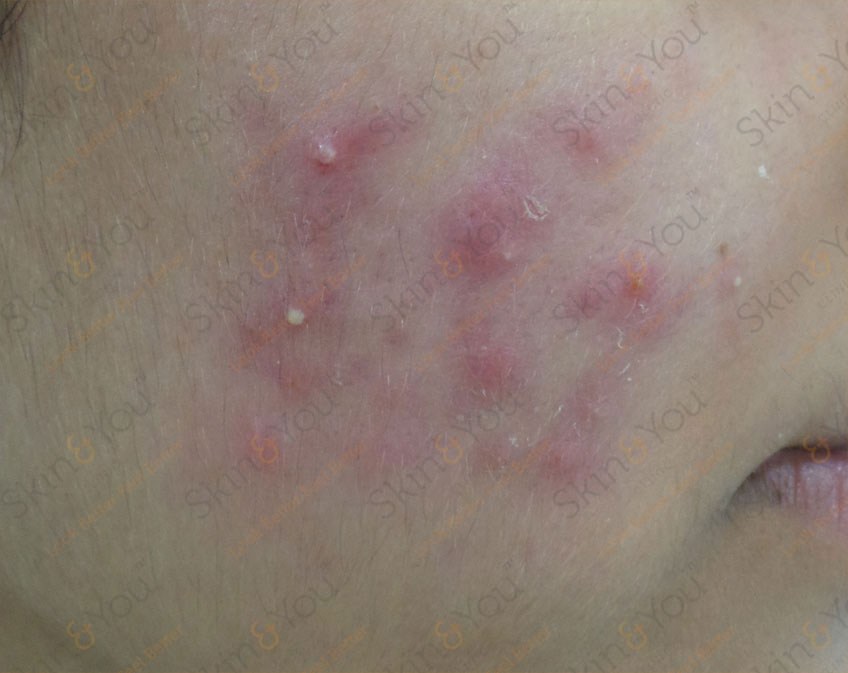
ACNE
Acne, or acne vulgaris, is a skin problem that starts when oil and dead skin cells clog up your pores. Some people call it blackheads, blemishes, whiteheads, pimples, or zits. When you have just a few red spots, or pimples, you have a mild form of acne.
Ask a Question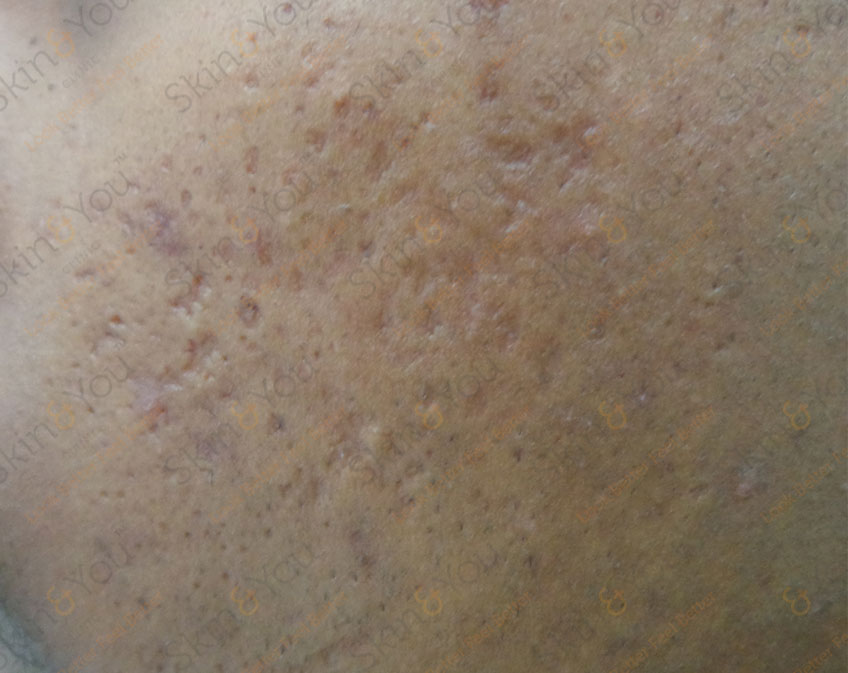
ACNE SCARS
Acne scars are usually the result of inflamed acne or nodular acne caused by skin glands engorged with excess oil, dead skin cells and bacteria. The pore swells, causing a break in the follicle wall.
Ask a Question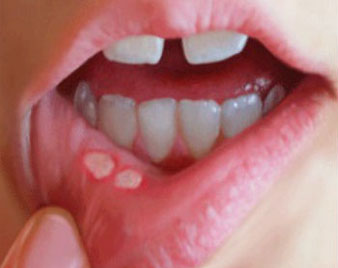
MOUTH ULCER
A mouth ulcer (also termed an oral ulcer or a mucosal ulcer) is an ulcer that occurs on the mucous membrane of the oral cavity. Mouth ulcers are very common, occurring in association with many diseases.
Ask a Question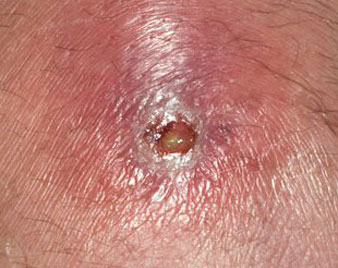
SKIN INFECTIONS
Skin infections are caused by staphylococcus or streptococcus organisms. The area may be painful, red tender to touch. A boil is a skin infection that starts in a hair follicle or oil gland.
Ask a Question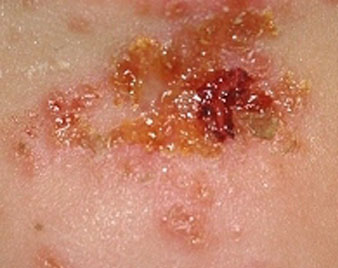
IMPETIGO
Impetigo is one of the most common skin infections in children. Impetigo is caused by the staphylococcus aureus, or more rarely streptococcus pyogenes bacteria. It can occur in adults but is seen far more often in children. Impetigo is contagious and can be spread to others through close contact or by sharing towels, sheets, clothing, toys, or other items.
Ask a Question
FOLLICULITIS
Folliculitis is an inflammation of the hair follicles. Each hair on your body grows out of a tiny pouch called a follicle. You can have folliculitis on any part of your body that has hair. But it is most common on the beard area, arms, back, buttocks, and legs.
Ask a Question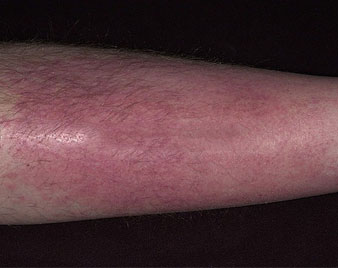
CELLULITIS
Cellulitis is a spreading bacterial infection of the skin and tissues beneath the skin. Staphylococcus and Streptococcus are the types of bacteria that are usually responsible for cellulitis, although many types of bacteria can cause the condition.
Ask a Question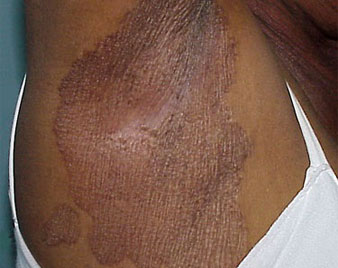
ERYTHRASMA
Erythrasma is a common chronic skin condition affecting the skin folds. The slowly enlarging patches of pink to brown dry skin are caused by an infection by the bacterium Corynebacterium minutissimum.
Ask a Question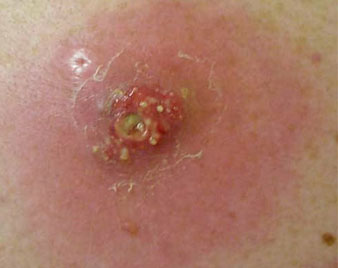
CARBUNCLE
A carbuncle is a cluster of boils, draining pus onto the skin. It is usually caused by bacterial infection.
Ask a Question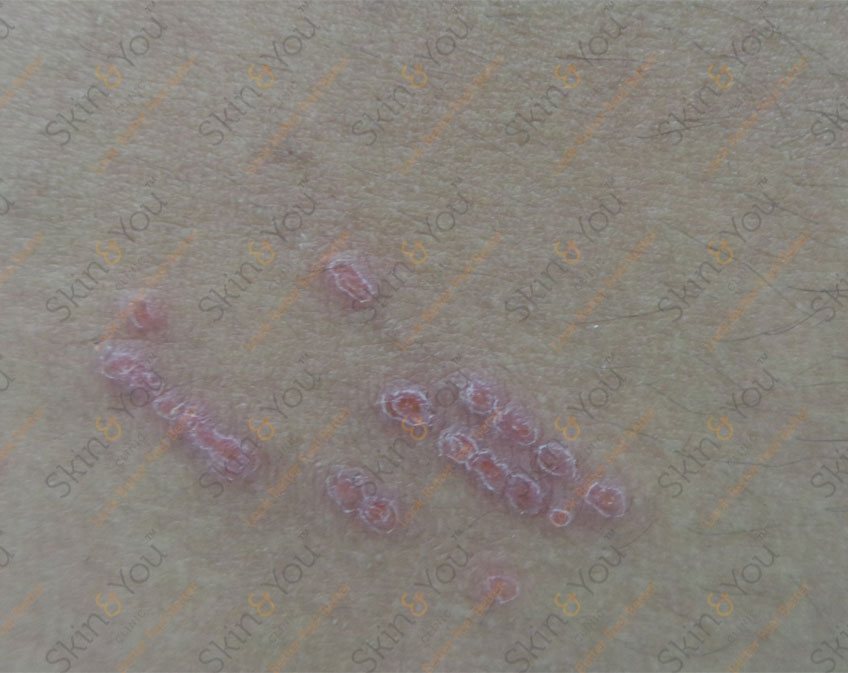
BITES & STINGS
Most reactions to insect bites and stings are mild, causing little more than redness, itching, stinging or minor swelling. Rarely, insect bites and stings, such as from a bee, a wasp, a hornet, a fire ant or a scorpion, can result in severe reactions.
Ask a Question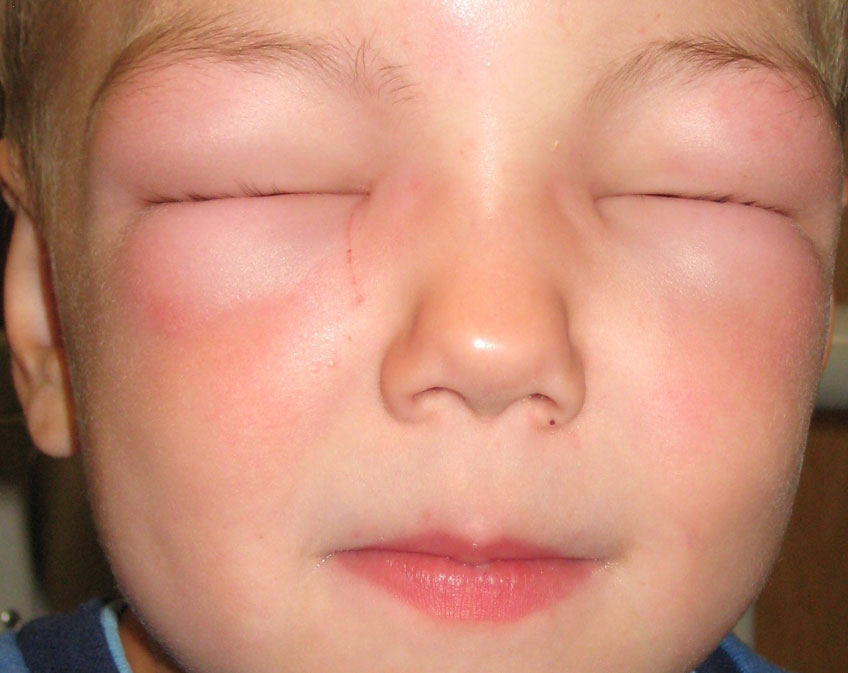
ANGIOEDEMA
Angioedema is a skin reaction similar to hives or urticaria. It is most often characterised by an abrupt and short-lived swelling of the skin and mucous membranes. All parts of the body may be affected but swelling most often occurs around the eyes and lips.
Ask a Question
BURN
A burn is damage to your body's tissues caused by heat, chemicals, electricity, sunlight or radiation. Scalds from hot liquids and steam, building fires and flammable liquids and gases are the most common causes of burns.
Ask a Question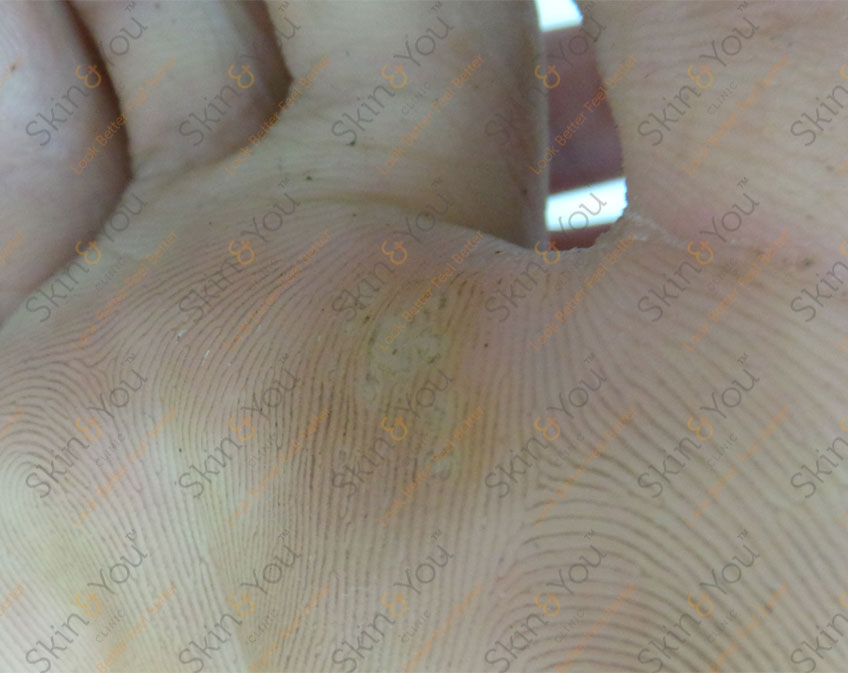
CORNS & CALLUS
Corns and calluses are hard, thickened areas of skin that form as a consequence of rubbing, friction or pressure on the skin.
Corns and calluses form on the feet and can make walking painful.
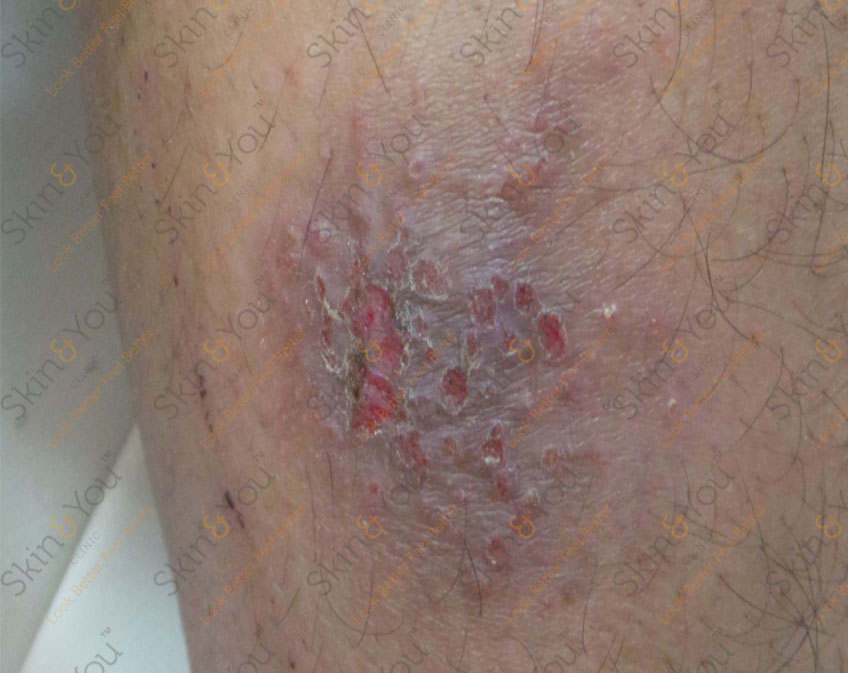
DERMATITIS
Dermatitis is inflammation of the skin. Depending on the type of dermatitis, areas of skin may become red and itchy with some acute attacks causing crusty scales or blisters that ooze fluid.
Ask a Question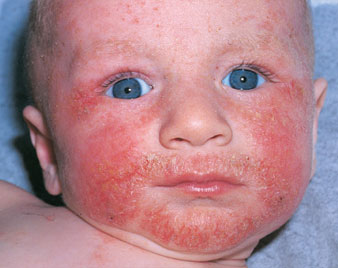
ATOPIC DERMATITIS
Atopic dermatitis (eczema) is a condition that makes your skin red and itchy. It's common in children but can occur at any age. Atopic dermatitis is long lasting (chronic) and tends to flare periodically and then subside. It may be accompanied by asthma or hay fever.
Ask a Question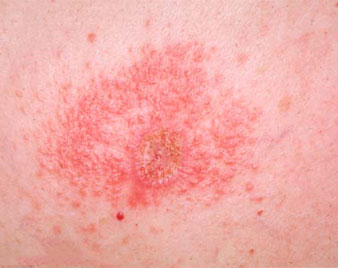
IRRITANT CONTACT DERMATITIS
Irritant contact dermatitis is a form of contact dermatitis, in which the skin is injured by friction, environmental factors such as cold, over-exposure to water, or chemicals such as acids, alkalis, detergents and solvents.
Ask a Question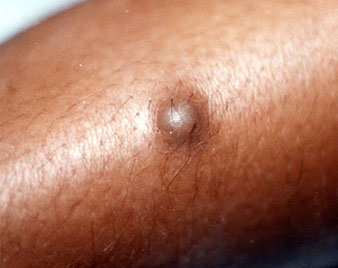
DERMATOFIBROMAS
Dermatofibromas are small, non-cancerous growths on the skin. The skin has several layers, including the fat cells, epidermis, and dermis. When the cells of the dermis layer overgrow, dermatofibromas can develop.
Ask a Question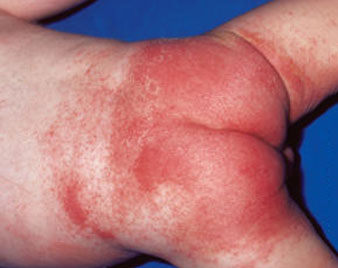
DIAPER RASH
Diaper rash is a common form of inflamed skin (dermatitis) that appears as a patchwork of bright red skin on your baby's bottom.
Diaper rash is often related to wet or infrequently changed diapers & skin sensitivity. It usually affects babies, though anyone who wears a diaper regularly can develop the condition.
DRUG ERUPTION ALLERGY
An adverse drug reaction is any unintended or undesirable response to a medication given at an appropriate dose. Predictable adverse drug reactions, including toxicity, side effects, and drug interactions, are dose dependent and related to the pharmacologic actions of the drug.
Ask a Question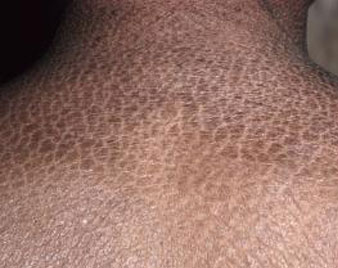
ICTHYOSIS VULGARIS
Ichthyosis vulgaris is a skin condition that causes dry, dead skin cells to accumulate in patches on the surface of your skin. It’s also known as “fish scale disease” because the dead skin accumulates in a similar pattern to a fish’s scales.
Ask a Question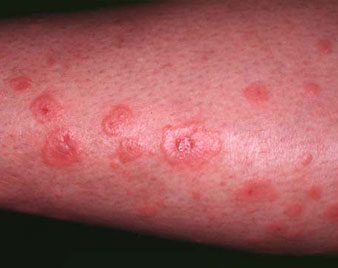
ERYTHEMA MULTIFORME
Erythema multiforme is a hypersensitivity reaction usually triggered by infections, most commonly herpes simplex virus (HSV). It presents with a skin eruption characterised by a typical target lesion. There may be mucous membrane involvement. It is acute and self-limiting, usually resolving without complications.
Ask a Question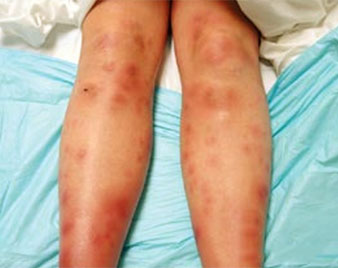
ERYTHEMA NODOSUM
Erythema nodosum is a type of skin inflammation that is located in a part of the fatty layer of skin. Erythema nodosum results in reddish, painful, tender lumps most commonly located in the front of the legs below the knees. The tender lumps, or nodules, of erythema nodosum range in size from a dime to a quarter. They may be inflamed off and on for a period of weeks, then shrink and become flat, leaving a bruised appearance.
Ask a Question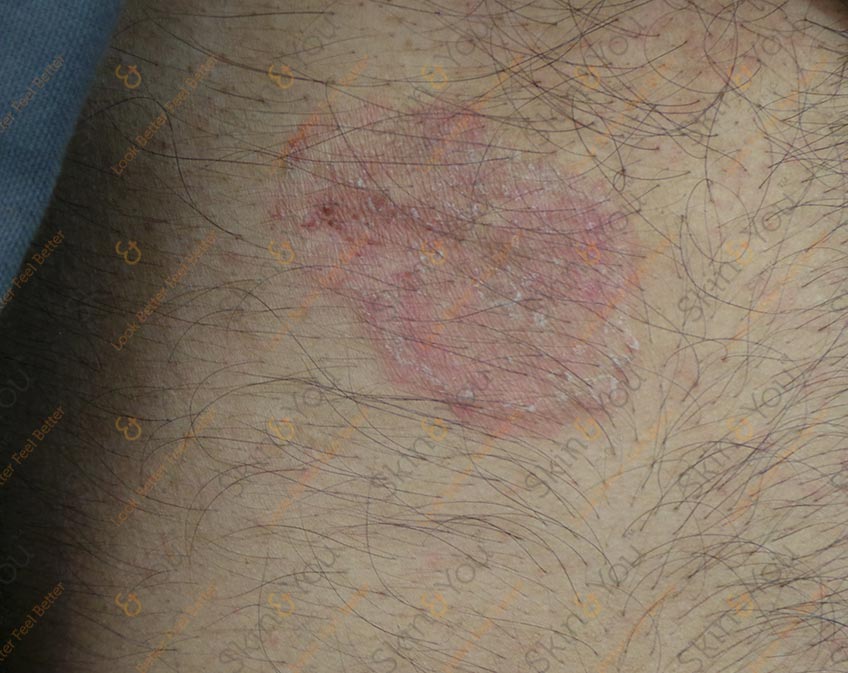
FUNGAL INFECTION
Fungal infections of the skin are very common and include athlete's foot, jock itch, ringworm, and yeast infections.
Ask a Question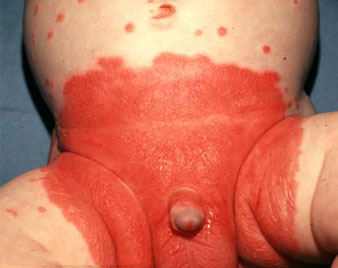
CANDIDIASIS
Candidiasis is a fungal infection due to any type of Candida (a type of yeast). When it affects the mouth, it is commonly called thrush. Signs and symptoms include white patches on the tongue or other areas of the mouth and throat. Other symptoms may include soreness and problems swallowing. When it affects the vagina, it is commonly called a yeast infection. Signs and symptoms include genital itching, burning, and sometimes a white "cottage cheese-like" discharge from the vagina. Less commonly the penis may be affected, resulting in itchiness.
Ask a Question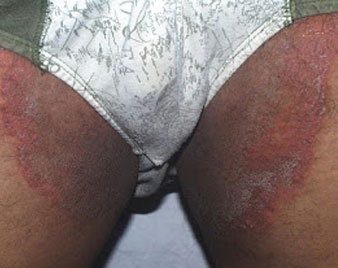
TINEA CRURIS
Jock itch, also called tinea cruris, is a common skin infection that is caused by a type of fungus called tinea. The fungus thrives in warm, moist areas of the body and as a result, infection can affect the genitals, inner thighs and buttocks. Infections occur more frequently in the summer or in warm, wet climates. Jock itch appears as a red, itchy rash that is often ring-shaped.
Ask a Question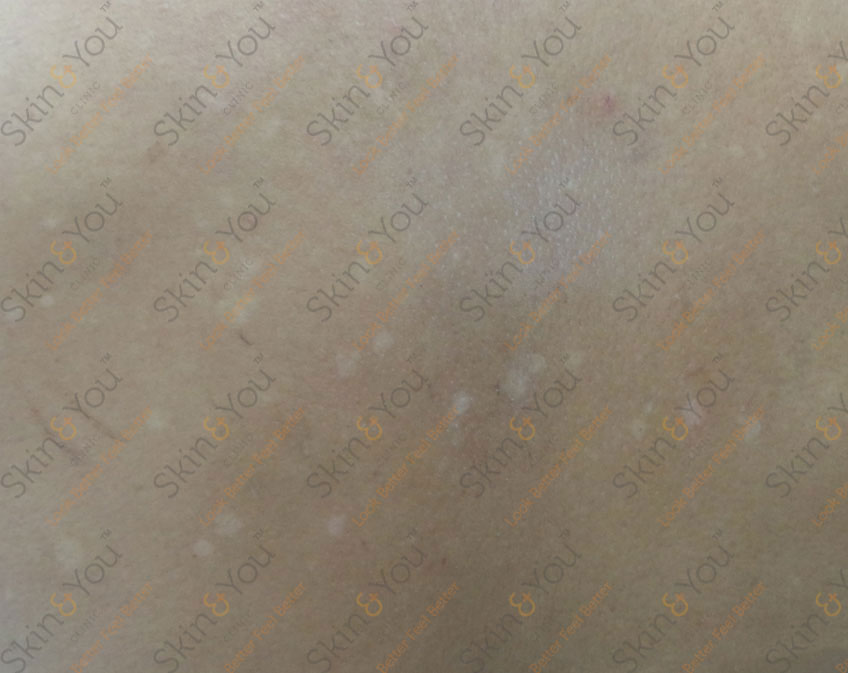
TINEA VERSICOLOR
Tinea versicolor is a fungal infection of the skin. It's also called pityriasis versicolor and is caused by a type of yeast that naturally lives on your skin. When the yeast grows out of control, the skin disease, which appears as a rash, is the result.
Ask a Question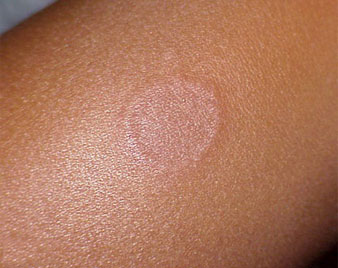
GRANULOMA ANNULARE
Granuloma annulare (GA) is a common condition of unknown cause. It appears most often over knuckles and other joints or in places that are subject to frequent, mild injury such as the back of the hands or top of the feet. It is seen most often in older children and young adults.
Ask a Question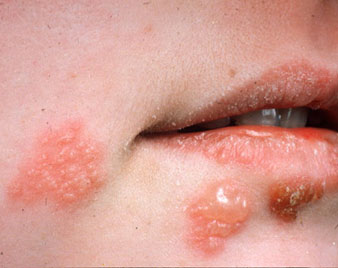
HERPES
Herpes is an infection that is caused by a herpes simplex virus (HSV). Oral herpes causes cold sores around the mouth or face. Genital herpes affects the genitals, buttocks or anal area. Genital herpes is a sexually transmitted disease (STD). It affects the genitals, buttocks or anal area. Other herpes infections can affect the eyes, skin, or other parts of the body. The virus can be dangerous in newborn babies or in people with weak immune systems.
Ask a Question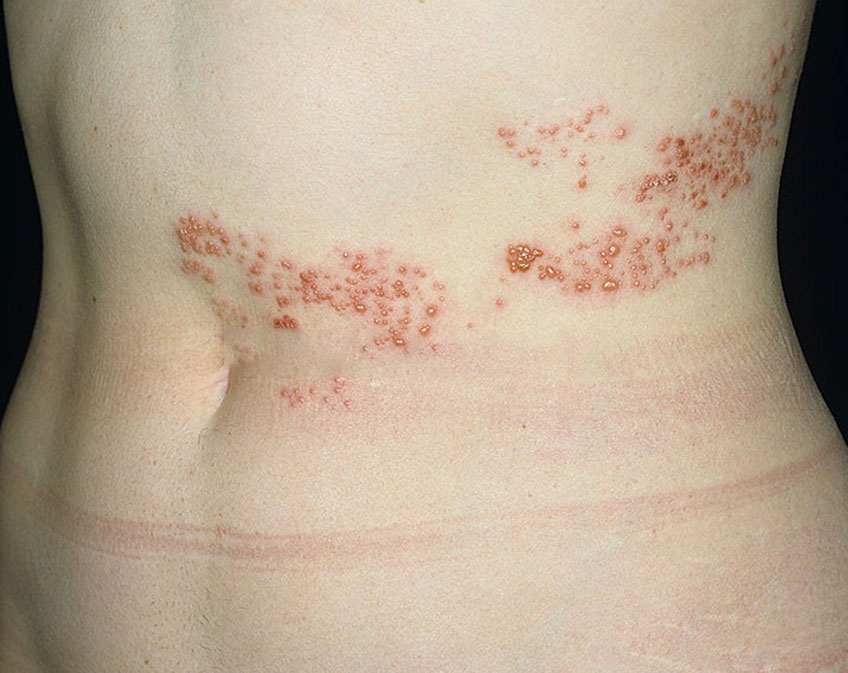
HERPES ZOSTER
Shingles, or herpes zoster, is a viral infection caused by the chickenpox virus. Symptoms include pain and a rash on one side of the body. Shingles most commonly affects older adults and people with weak immune systems.
Ask a Question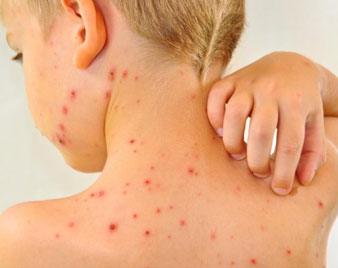
CHICKENPOX (VARICELLA)
Chickenpox (varicella) is a contagious illness that causes an itchy rash and red spots or blisters (pox) all over the body. Chickenpox can cause problems for pregnant women, newborns, teens and adults, and people who have immune system problems that make it hard for the body to fight infection.
Ask a Question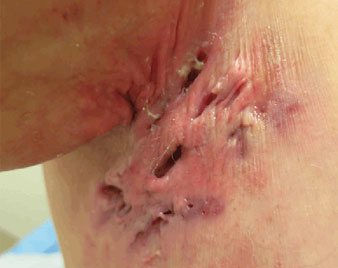
HIDRADENITIS SUPPURATIVA
Hidradenitis suppurativa is a chronic skin condition that features pea-sized to marble-sized inflammation of glands under the skin. Also known as acne inversa, these deep-seated nodular abscess typically develop where skin rubs together — such as the armpits, groin, between the buttocks and under the breasts.
Ask a Question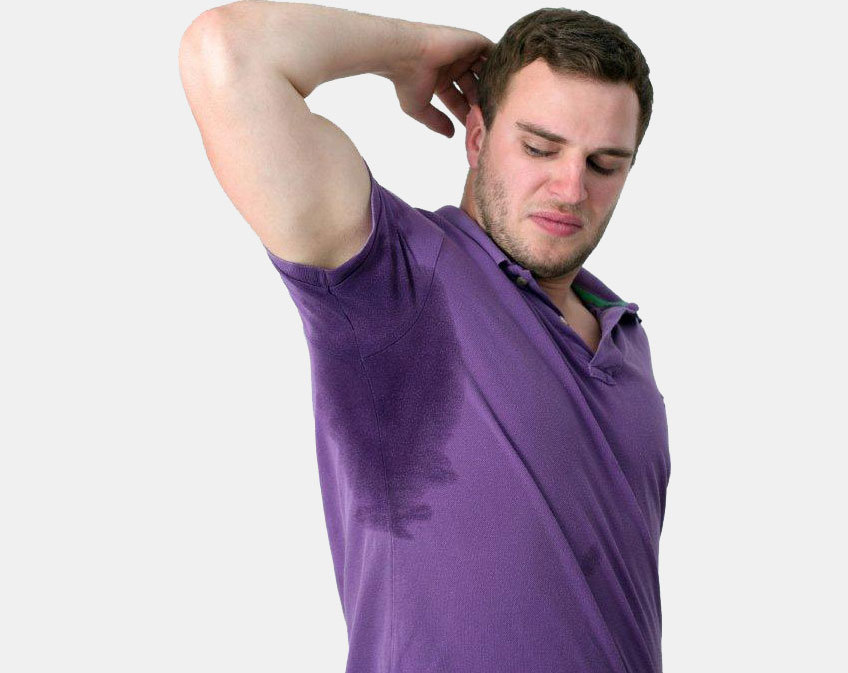
HYPERHIDROSIS
Hyperhidrosis, which is sweating in excess of that required for normal thermoregulation, is a condition that usually begins in either childhood or adolescence. Although any site on the body can be affected by hyperhidrosis, the sites most commonly affected are the palms, soles, and axillae.
Ask a Question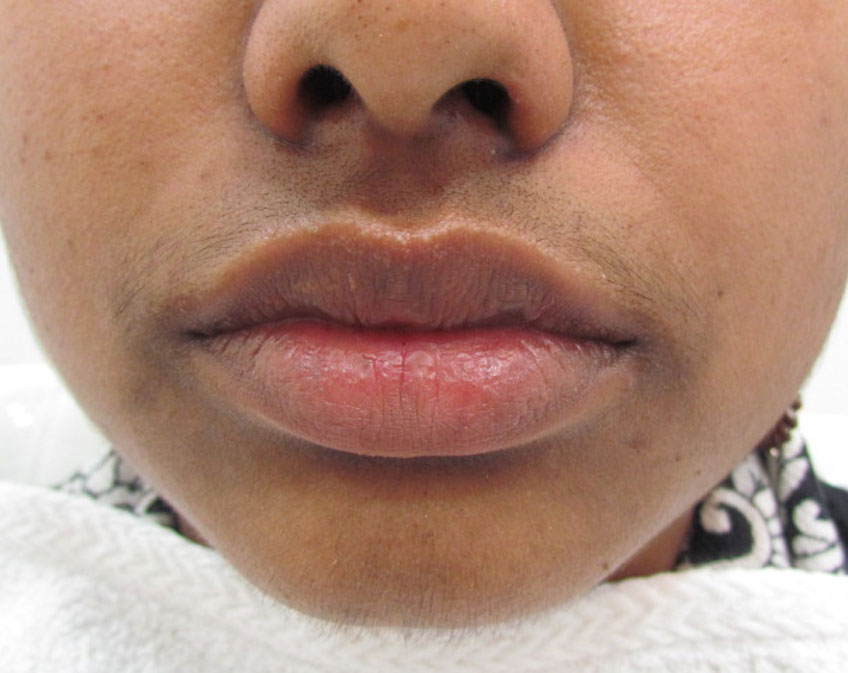
HYPERTRICHOSIS
Hypertrichosis is excessive hair growth over and above the normal for the age, sex and race of an individual, in contrast to hirsutism, which is excess hair growth in women following a male distribution pattern. Hypertrichosis can develop all over the body or can be isolated to small patches. Hypertrichosis may be congenital (present at birth) or acquired (arises later in life).
Ask a Question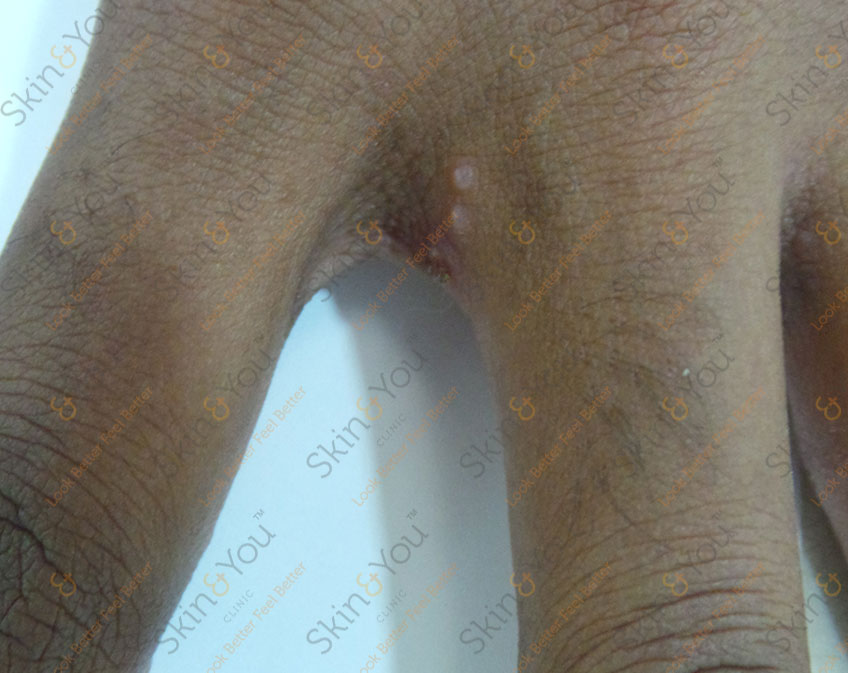
SCABIES
Scabies is a skin infestation caused by a tiny microscopic bug known as the human itch mite. This mite is usually passed from skin to skin. It can also be transmitted through infested clothing or bedding.
The most common symptoms of scabies are intense itching and a pimple-like skin rash. The scabies mite usually is spread by direct, prolonged, skin-to-skin contact with a person who has scabies. Scabies can spread rapidly under crowded conditions where close body contact is frequent. Institutions such as nursing homes, extended-care facilities are often sites of scabies outbreaks.
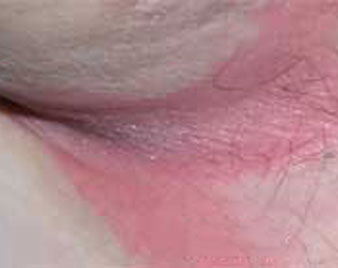
INTERTRIGO
Intertrigo describes a rash in the body folds, such as behind the ears, in the folds of the neck, under the arms (axillae), under a protruding abdomen, in the groin, between the buttocks, in the finger webs or toe spaces. Although Intertrigo may affect one skin fold, it is common for it to involve multiple sites.
Ask a Question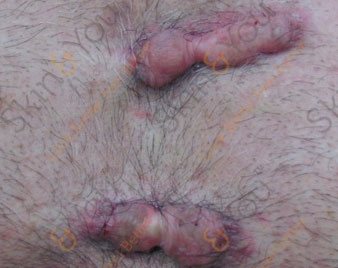
KELOID OR HYPERTROPHIC SCAR
When skin is injured, fibrous tissue, called scar tissue, forms over the wound to repair and protect the injury. In some cases, scar tissue grows excessively, forming smooth, hard growths called keloids. Keloids can be much larger than the original wound. They’re most commonly found on the chest, shoulders, earlobes, and cheeks. However, keloids can affect any part of the body.
Although keloids aren’t harmful to your health, they may create cosmetic concerns.
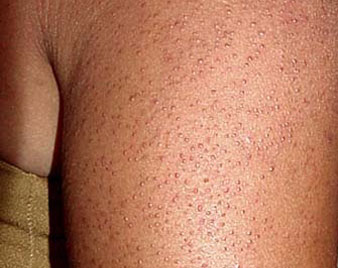
KERATOSIS PILARIS
Keratosis pilaris is a common, harmless skin condition. It causes small, hard bumps that may make your skin feel like sandpaper.
Keratosis pilaris is a common skin condition that causes rough patches and small, acne-like bumps, usually on the arms, thighs, cheeks and buttocks. Keratosis pilaris bumps are usually white, sometimes red, and generally don't hurt or itch. Keratosis pilaris can be frustrating because it's difficult to treat.
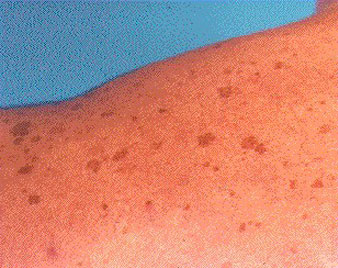
LENTIGO
A type of freckle that is a small tan, brown, or black spot which tends to be darker than the usual freckle and which do not fade in the winter. This kind of spot is referred to as lentigo simplex.
Ask a Question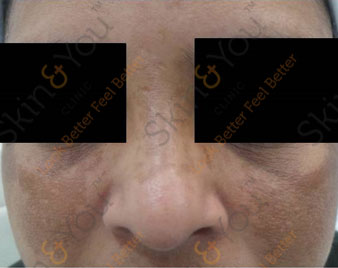
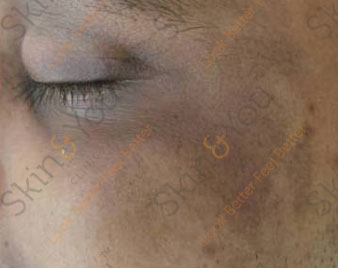
MELASMA
Melasma are patches of dark skin that appear on areas of the face that are exposed to the sun. Melasma is a common skin problem. It causes brown to gray-brown patches on the face. Most people get it on their cheeks, bridge of their nose, forehead, chin, and above their upper lip. It also can appear on other parts of the body that get lots of sun, such as the forearms and neck.
Ask a Question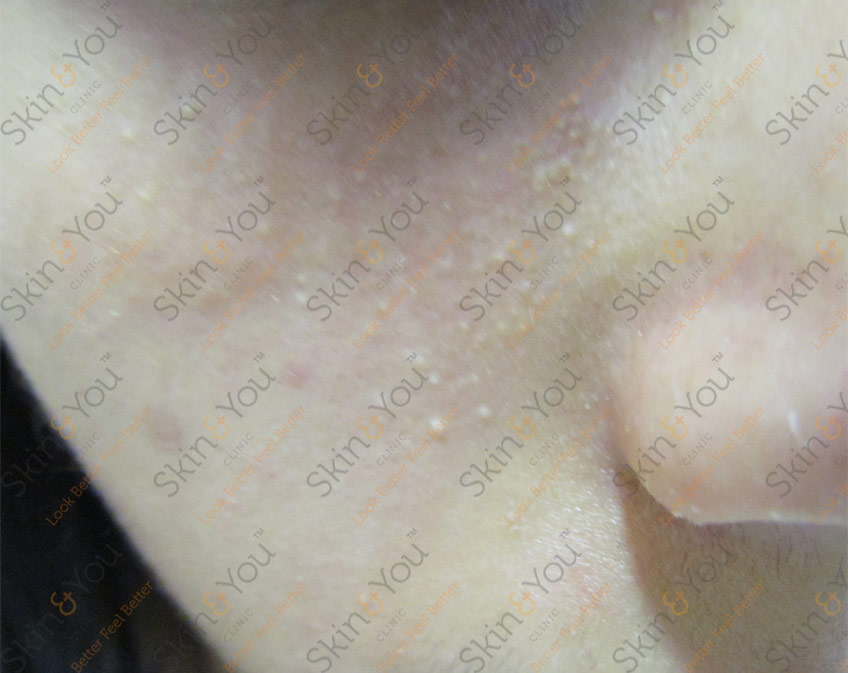
MILIA
Milia are commonly found on the skin of people of all ages. They are formed when keratin (a substance produced by the skin) becomes entrapped beneath the outer layer of the skin, forming a tiny cyst. Milia are tiny white bumps or small cysts on the skin. They are almost always seen in newborn babies.
Ask a Question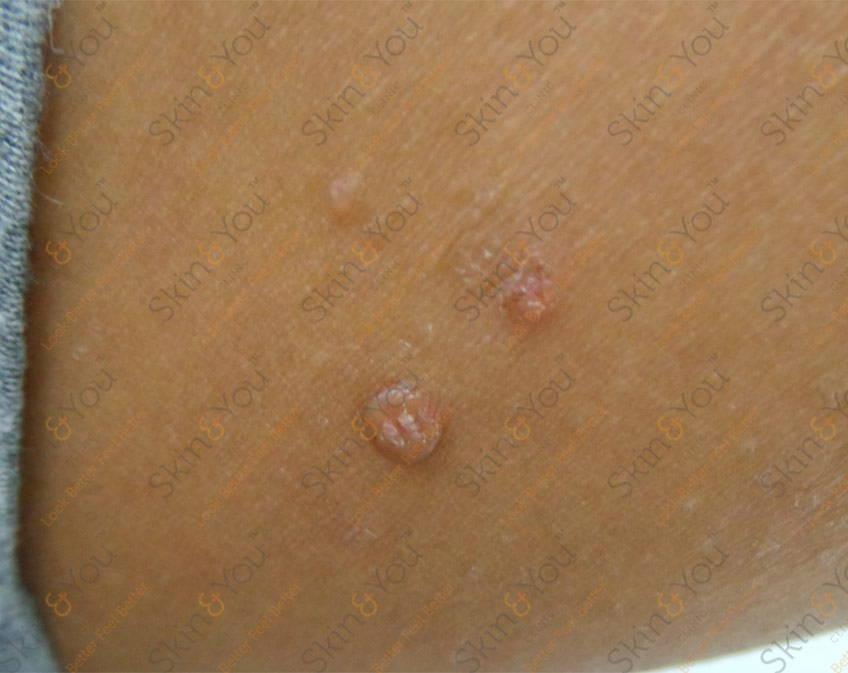
MOLLUSCUM CONTAGIOSUM
Molluscum contagiosum is a relatively common viral infection of the skin that results in round, firm, painless bumps ranging in size from a pinhead to a pencil eraser. If the bumps are scratched or injured, the infection can spread to surrounding skin. Though most common in children, Molluscum can affect adults as well - particularly those with weakened immune systems.
Ask a Question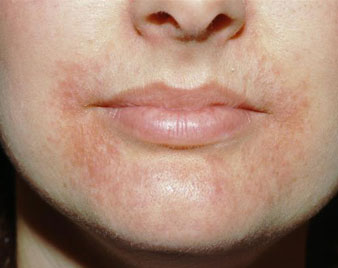
PERIORAL DERMATITIS
Perioral dermatitis is a common facial skin problem in which groups of itchy or tender small red papules (bumps) appear around the mouth. The papules spare the skin bordering the lips (which then appears pale) but develop on the sides of the chin, and then spread to include upper lip and cheeks. The surrounding skin may be pink, and the skin surface often becomes dry and flaky.
Ask a Question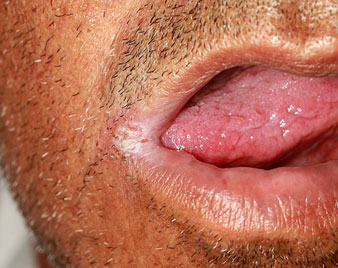
PERLECHE
Angular cheilitis single or multiple fissures and cracks at the corner of the mouth on one side or both sides, which in advanced stagesmay spread to the lips and cheeks. Causes include primary or superimposed infection with microorganisms such as Candida albicans,staphylococci, or streptococci; poor hygiene; drooling of saliva; overclosure ofthe jaws in patients without teeth or with ill-fitting dentures, nutritional deficiencies are a few causes of perleche.
Ask a Question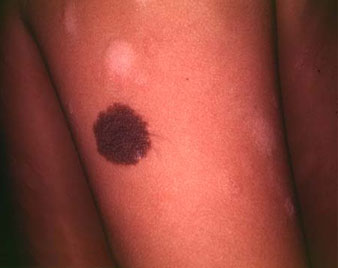
PITYRIASIS ROSEA
Pityriasis rosea is a viral rash which lasts about 6–12 weeks. It is characterised by a herald patch followed by similar, smaller oval red patches that are located mainly on the chest and back. It is a common skin disease that causes a rash. This rash usually disappears on its own without treatment. Sometimes the rash lasts much longer.
Ask a Question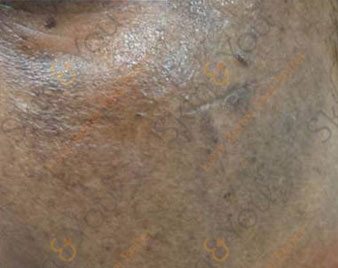
POST INFLAMMATORY PIGMENTATION
Post inflammatory pigmentation is temporary pigmentation that follows injury (e.g. thermal burn) or inflammatory disorder of the skin (e.g. dermatitis, infection). It is mostly observed in darker skin types. More severe injury results in post inflammatory hypopigmentation, which is usually permanent.
Ask a Question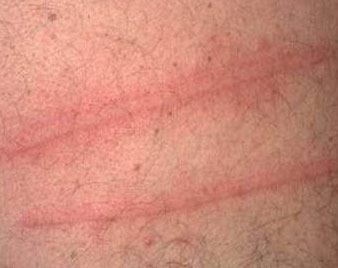
PRURITUS
Post inflammatory pigmentation is temporary pigmentation that follows injury (e.g. thermal burn) or inflammatory disorder of the skin (e.g. dermatitis, infection). It is mostly observed in darker skin types. More severe injury results in post inflammatory hypopigmentation, which is usually permanent.
Ask a Question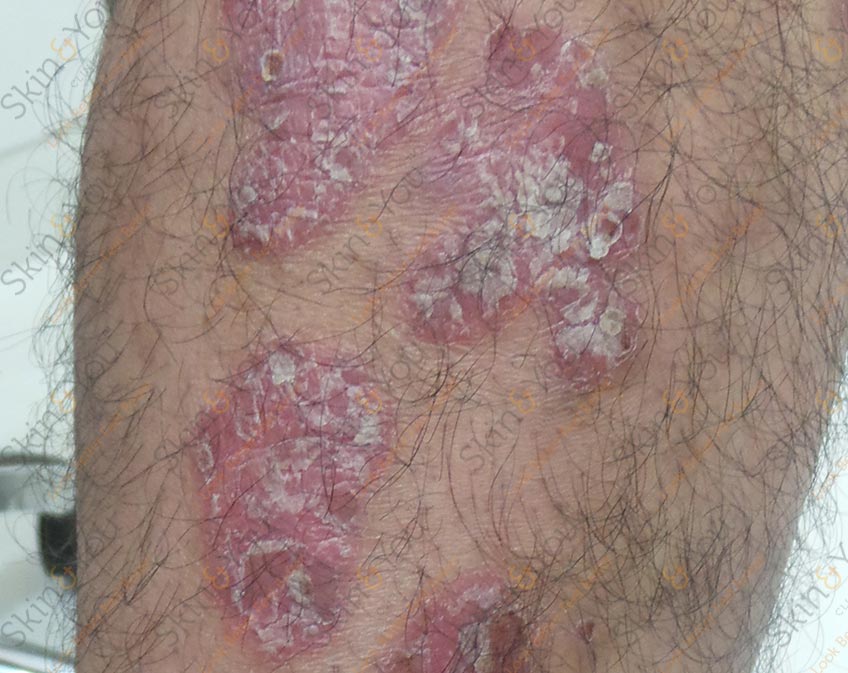
PSORIASIS
Psoriasis is a long-lasting autoimmune disease characterized by patches of abnormal skin. These skin patches are typically red, itchy, and scaly. They may vary in severity from small and localized to complete body coverage. Injury to the skin can trigger psoriatic skin changes at that spot, which is known as Koebner phenomenon.
Ask a Question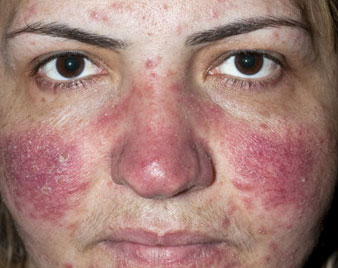
ROSACEA
Rosacea is a common skin condition that causes redness in your face and often produces small, red, pus-filled bumps. Although rosacea can occur in anyone, it most commonly affects middle-aged women who have fair skin.
Ask a Question
SEBORRHEIC DERMATITIS
Seborrheic dermatitis is a skin disorder affecting the scalp, face, and torso. Typically, seborrheic dermatitis presents with scaly, flaky, itchy, and red skin. It particularly affects the sebaceous-gland-rich areas of skin. In adolescents and adults, seborrhoeic dermatitis usually presents on scalp scaling similar to dandruff or as mild to marked erythema of the nasolabial fold.
Ask a Question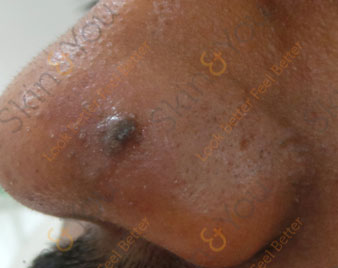
NEVUS OR MOLE
Nevus, also known as a mole is the medical term for sharply circumscribed and chronic lesions of the skin or mucosa. These lesions are commonly named birthmarks or beauty marks. Nevi are benign by definition. However, 25% of malignant melanomas (a skin cancer) arise from pre-existing nevi.
Ask a Question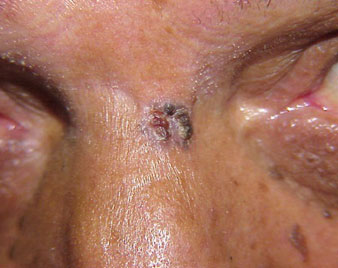
SKIN CANCERS
Skin cancers are cancers that arise from the skin. They are due to the development of abnormal cells that have the ability to invade or spread to other parts of the body. There are three main types: basal-cell cancer (BCC), squamous-cell cancer (SCC) and melanoma.
Ask a Question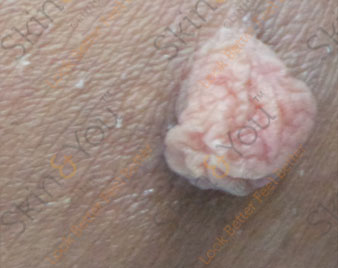
SKIN TAGS
Skin tags are common, acquired benign skin growths that look like small, soft balloons of hanging skin. Skin tags are harmless growths that can vary in number from one to hundreds. Males and females are equally prone to developing skin tags. Obesity is associated with skin tag development. Although some skin tags may fall off spontaneously, most persist once formed. The medical name for skin tag is acrochordon.
Ask a Question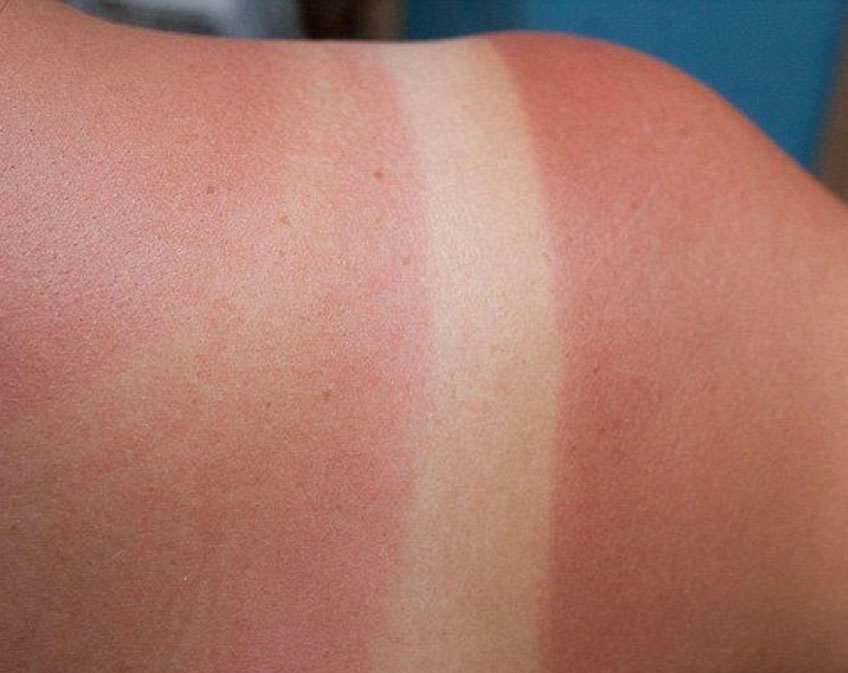
SUNBURN
Sunburn — red, painful skin that feels hot to the touch — usually appears within a few hours after too much exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light from sunshine or artificial sources, such as sunlamps. Sunburn may take several days or longer to fade.
Ask a Question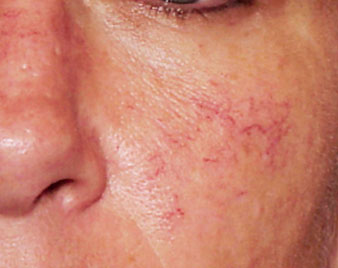
TELANGIECTASIA
Telangiectasia are small, widened blood vessels on the skin. They are usually harmless, but may be associated with several diseases. They can occur due to unprotected excess sun exposure especially in fair skin individuals.
Telangiectasia may develop anywhere within the body. But they are most easily seen on the skin, mucous membranes, and whites of the eyes. Usually, they do not cause symptoms.

URTICARIA
Urticaria commonly referred to as hives, is a kind of skin rash notable for pale red, raised, itchy bumps. Hives may cause a burning or stinging sensation. They are frequently caused by allergic reactions; however, there are many nonallergic causes. Most cases of hives lasting less than six weeks (acute urticaria) are the result of an allergic trigger. Chronic urticaria (hives lasting longer than six weeks) is rarely due to an allergy.
The majority of chronic hives cases have an unknown (idiopathic) cause.
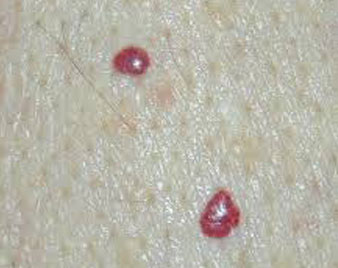
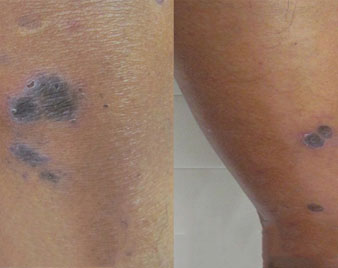
CHERRY ANGIOMA
A cherry angioma is a noncancerous (benign) skin growth made up of blood vessels.
Cherry angioma are fairly common skin growths that vary in size. They can occur almost anywhere on the body, but usually develop on the trunk.
They are most common after age 30. The cause is unknown, but they tend to be inherited (genetic).
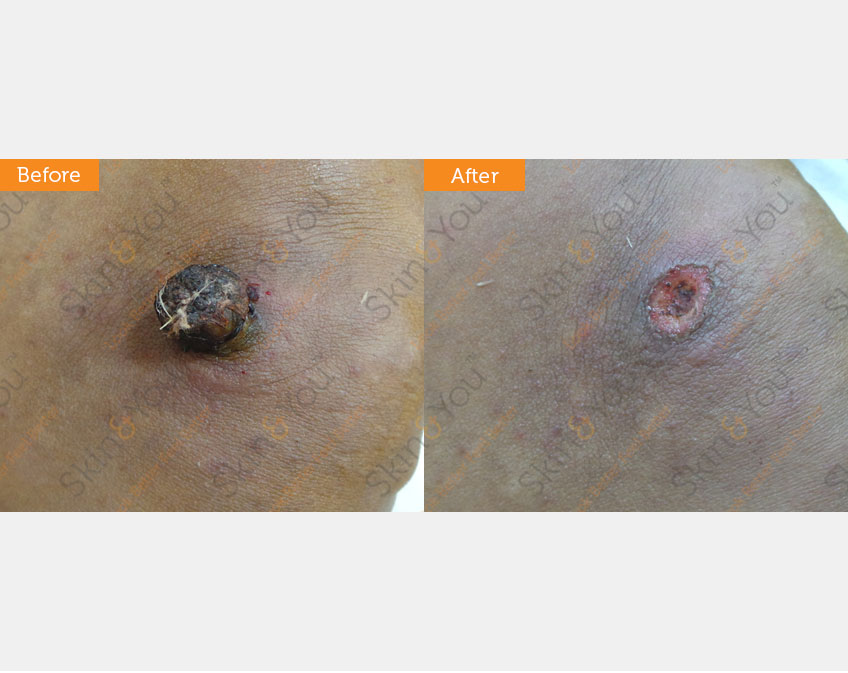
PYOGENIC GRANULOMA
Pyogenic granuloma is a relatively common skin growth. It is usually a small red, oozing and bleeding bump that looks like raw hamburger meat. It often seems to follows a minor injury and grows rapidly over a period of a few weeks to an average size of a half an inch. The head, neck, upper trunk and hands and feet are the most common sites.
Ask a Question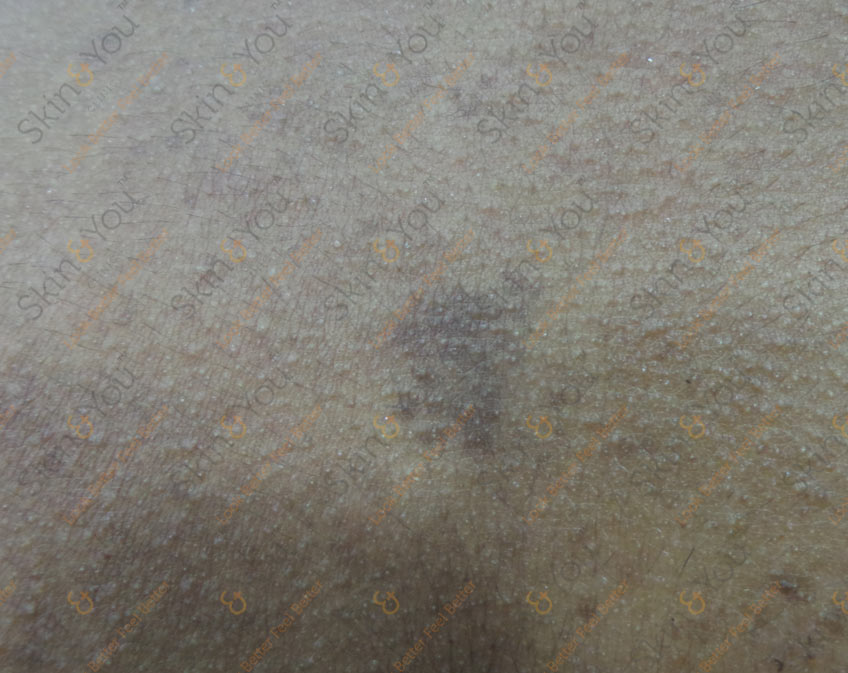
NEVUS SIMPLEX
Most common capillary malformation on infant present as a pink to red patch on the forehead, eyelid, perinasal area or nape of neck.
Ask a Question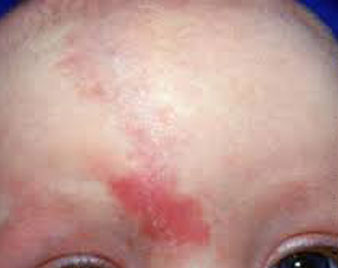
PORT-WINE STAIN
A port-wine stain is a birthmark in which swollen blood vessels create a reddish-purplish discoloration of the skin.
Ask a Question
NAEVUS
A naevus is a circumscribed and stable malformation of a component of the skin. Naevi are often present at birth, when they are often called birthmarks. Naevi composed of the pigment cells that produce melanin (melanocytes) are called melanocytic naevi.
Naevus of Ota, naevus of Ito and naevus of Hori are melanocytic naevi with slate-brown or blue/grey colouring. The nevus cells are found deep within the dermis, a form of dermal melanocytosis.
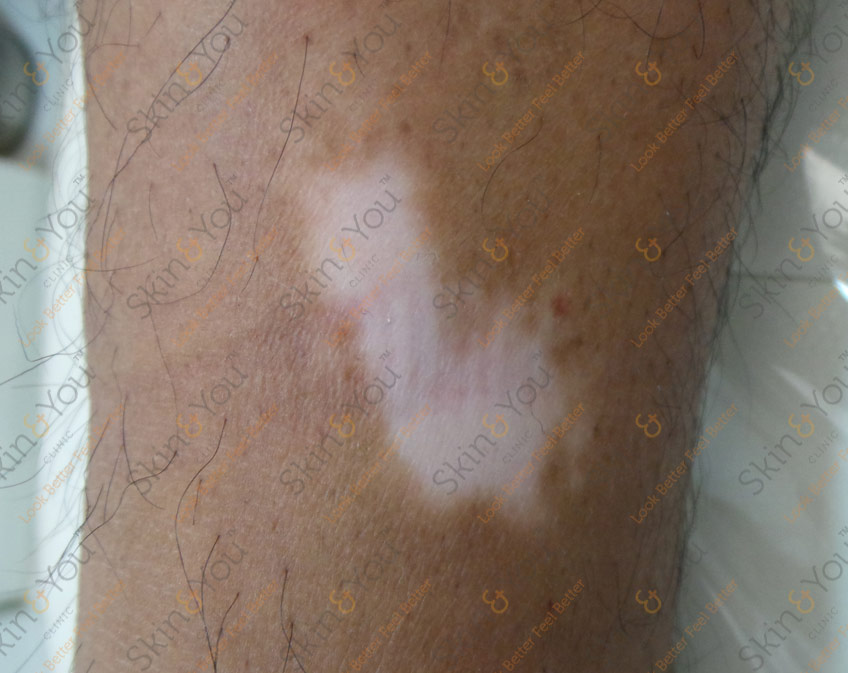
VITILIGO
Vitiligo is a chronic skin condition characterized by portions of the skin pigment. It occurs when skin pigment cells die or are unable to function. Aside from cases of contact with certain chemicals, the cause of vitiligo is unknown. Research suggests vitiligo may arise from autoimmune, genetic, oxidative stress, neural, or viral causes. Vitiligo is typically classified into two main categories: segmental and non-segmental vitiligo.
Ask a Question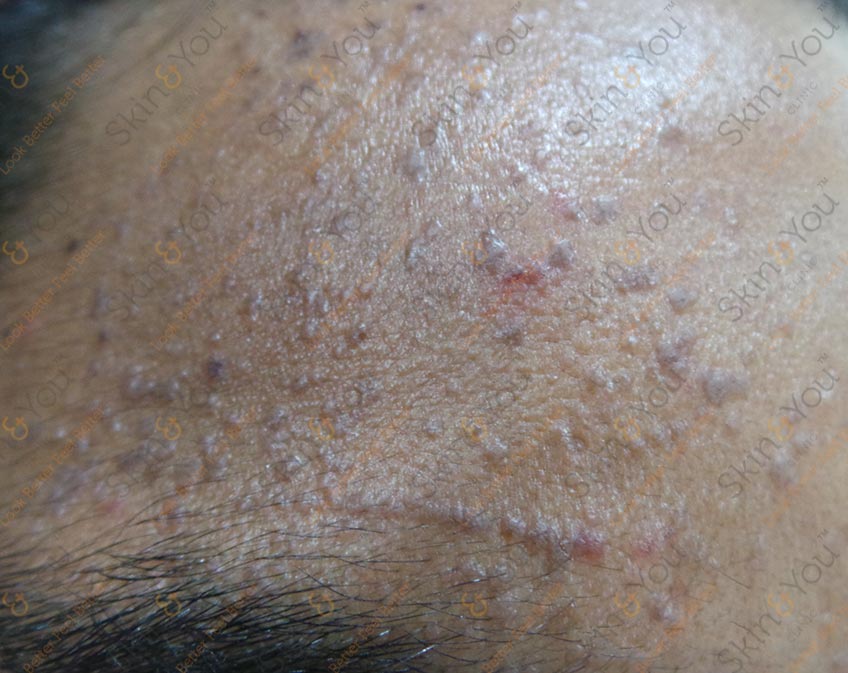
VIRAL WART
A wart is a small, rough growth resembling a cauliflower. It typically occurs on humans' hands or feet but often in other locations. Warts are caused by a viral infection, specifically by one of the Human papilloma virus (HPV). There are as many as 10 varieties of warts; the most common considered to be mostly harmless. It is possible to get warts from others; they are contagious and usually enter the body in an area of broken skin.
Ask a Question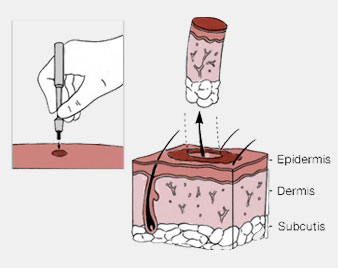
BIOPSY
A biopsy is a sample of tissue taken from the body in order to examine it more closely. A doctor should recommend a biopsy when an initial test suggests an area of tissue in the body isn't normal.
Doctors may call an area of abnormal tissue a lesion, a tumor, or a mass. These are general words used to emphasize the unknown nature of the tissue.
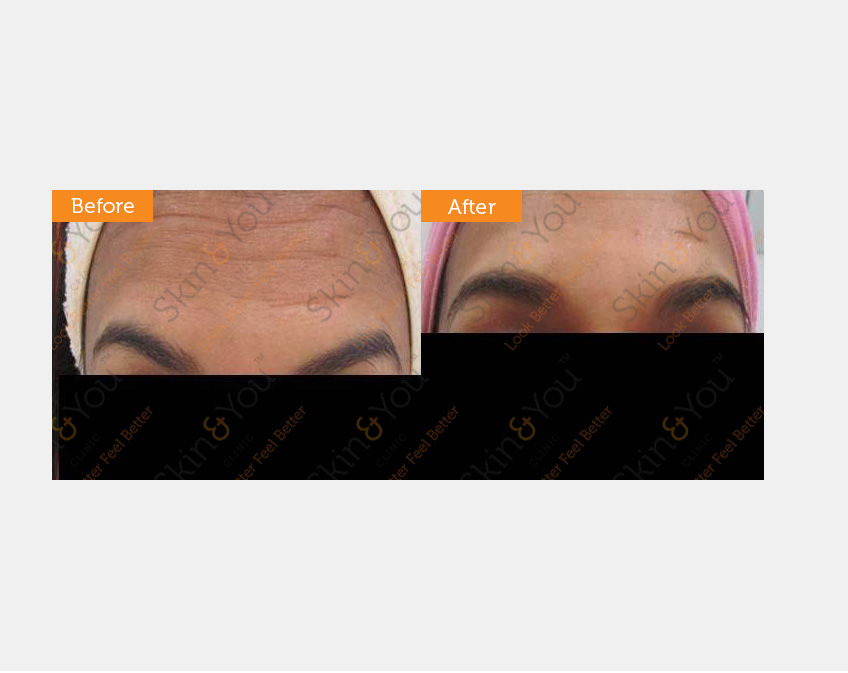
BOTULINUM TOXIN (BTX )
Botulinum toxin (BTX) is a protein. It is also produced commercially for medical, cosmetic, and research use.
In cosmetic applications, injection of botulinum toxin can be used to prevent development of wrinkles by paralyzing facial muscles. Following treatment, visible results of Botox Cosmetic are usually seen within 3–5 days, however it can take up to 2 weeks to see full results.
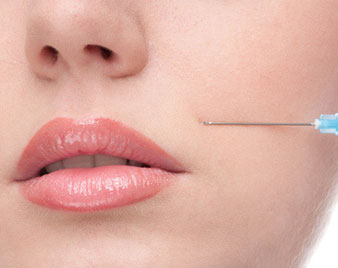
DERMAL FILLERS
Dermal fillers help to diminish facial lines and restore volume and fullness in the face.
Dermal fillers can be used to:
Plump thin lips, Enhance shallow contours, Soften facial creases and wrinkles, Improve the appearance of recessed scars
Dermal fillers can be very helpful in those with early signs of aging, or as a value-added part of facial rejuvenation surgery.
LICHEN PLANUS
Lichen planus is a rare form of lichen planus. It is characterized by oval or irregularly shaped brown to gray-brown macules and patches on the skin. Areas that are exposed to sun such as the forehead, temples and neck are most commonly affected. However, the macules and patches may also develop on the trunk or in places where two areas of skin touch or rub together (i.e. the armpit, groin, etc). LPP is a relapsing condition with periods of worsening symptoms separated by periods of a decrease in or disappearance of symptoms.
Ask a Question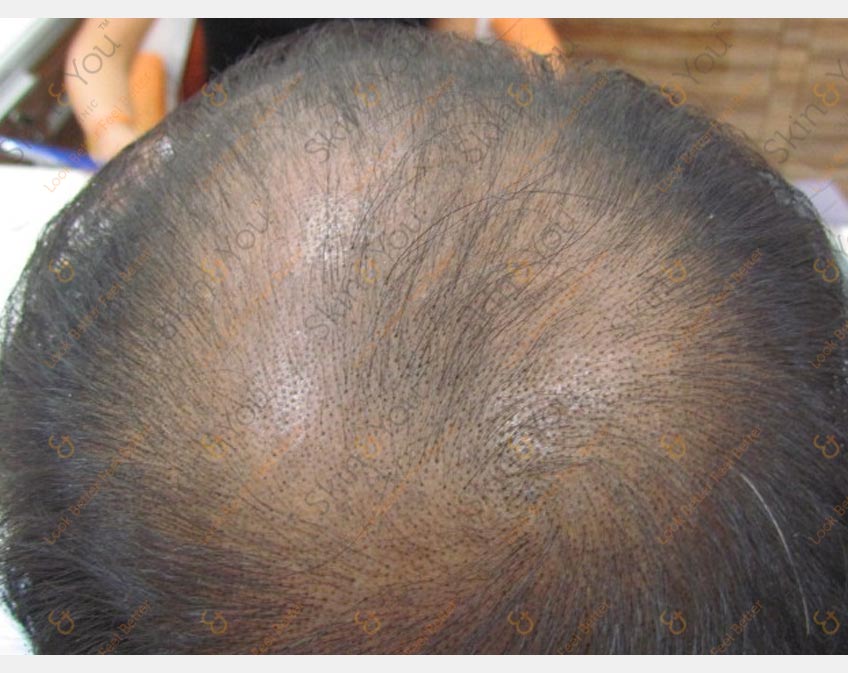
ANDROGENETIC ALOPECIA
Androgenetic alopecia is a common form of hair loss in both men and women. In men, this condition is also known as male-pattern baldness. Hair is lost in a well-defined pattern, beginning above both temples. Over time, the hairline recedes to form a characteristic "M" shape. Hair also thins at the crown (near the top of the head), often progressing to partial or complete baldness.
Ask a Question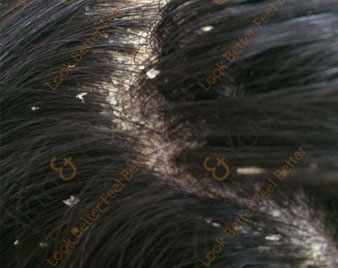
DANDRUFF
Dandruff is a common chronic scalp condition marked by flaking of the skin on your scalp. Although dandruff isn't contagious and is rarely serious, it can be embarrassing and sometimes difficult to treat.
Ask a Question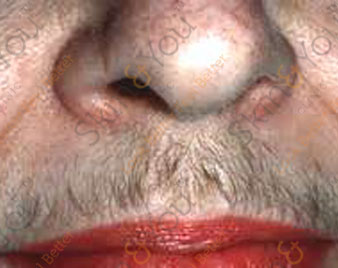
EXCESS HAIR
The normal amount of body hair for women varies. Most of the time, a woman only has fine hair, or peach fuzz, above the lips and on the chin, chest, abdomen, or back. If you have coarse, dark hairs in these areas, the condition is called hirsutism. Such hair growth is more typical of men.
Women normally produce low levels of male hormones (androgens). If your body makes too much of this hormone, you may have unwanted hair growth.
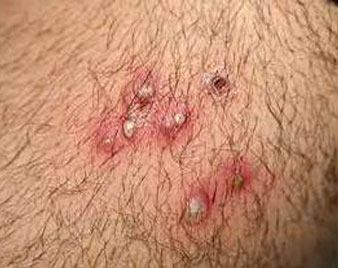
HAIR INFECTION
Folliculitis is an infection of the hair follicles in the skin. It is a common problem that is not usually serious. Tiny pus-filled spots (pustules) develop at the base of a hair, often in crops. Mild cases often resolve without treatment.
Ask a Question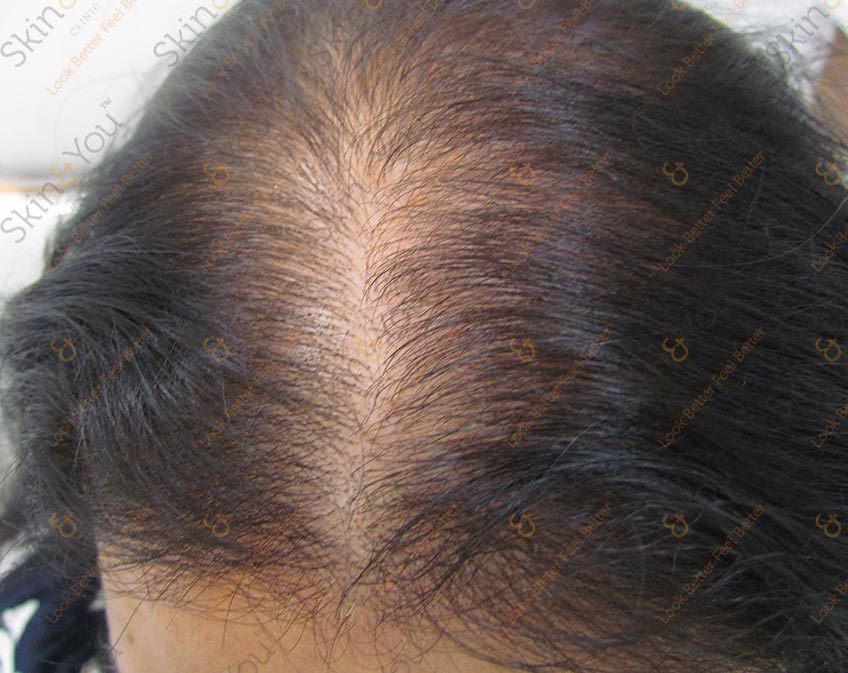
HAIR LOSS
Hair loss, also known as alopecia or baldness, refers to a loss of hair from the head or body. Baldness can refer to general hair loss or male pattern hair loss. Hair loss and hypotrichosis have many causes including androgenetic alopecia, fungal infection, trauma (e.g., due to (trichotillomania), radiotherapy, chemotherapy, nutritional deficiencies (e.g., iron deficiency) and autoimmune diseases such asalopecia areata.
Ask a Question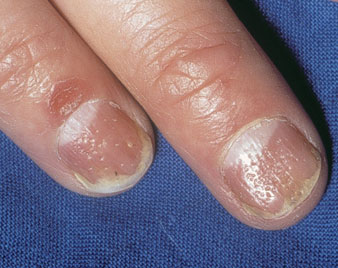
NAIL CHANGES
Often there are certain skin conditions where nail changes are seen as part of the disease process or as disease process involving nails only. These changes often help in clinching the diagnosis.
For example some of the changes in psoriasis: nail pitting, crumbling nail plate, roughened nails, distal onycholysis (separation of nail plate from nail bed), and subungual hyperkeratosis (i.e. Build-up of soft yellow keratin in the space created by the onycholysis)
In lichen planus: thinning, brittleness, crumbling of the nail with accentuated surface longitudinal ridging with either partial or complete loss of nail plate and formation of pterygium can be seen.
In alopecia areata: superficial nail pitting, brittle nails with vertical ridges, spoon like curvature of nails and separation of distal part of nail plate from nail bed can be seen
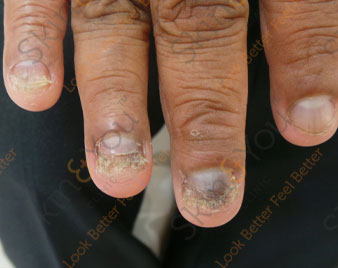
NAIL INFECTION
Nail infection are routinely encountered condition which can be caused by bacteria, fungal or mixed.
Most common causes are trauma, manicure or pedicures with unsterile tools, immunocompromised patients, diabetics, closed tight footwear, etc.
They are seen as yellowish or greenish black discolouration of nail plate, with or without loss of nail plate, separation of nail plate from underlying nail bed.
For treating this condition underlying cause have to be ruled out and if required fungal culture and sensitivity testing can be done.
Treatment is long duration: for finger nails minimum 3 months and toe nails minimum 6 months with topical and oral medications.
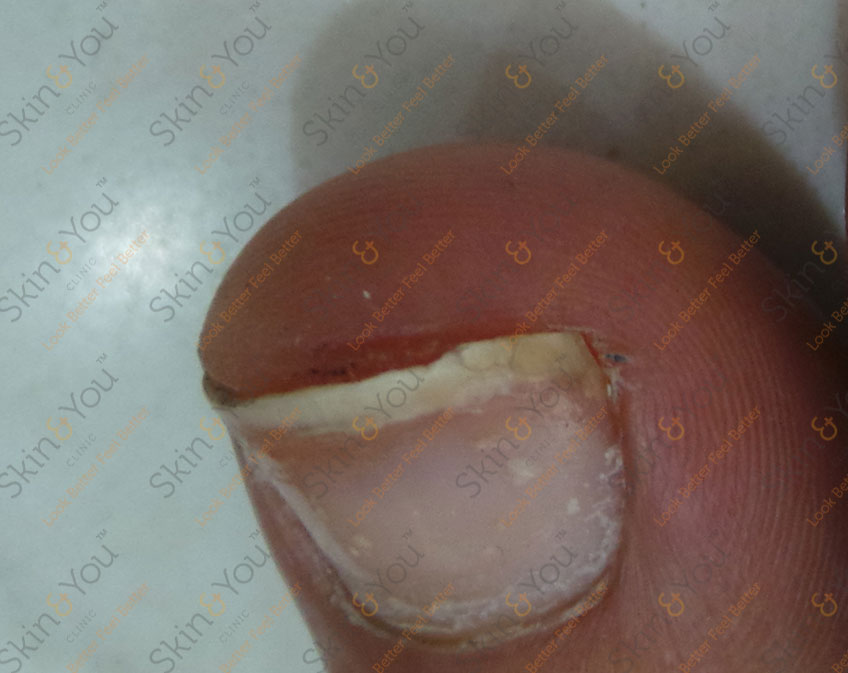

SPLITTING PEELING BRITTLE NAIL
Ridging of the Nail: Seen in lichen planus, injury to the nail
Brittle nails: Aging and certain diseases and conditions.
Splitting of nails/ onychoschizia: More common in women seen in vitamin deficiencies, and repeated wetting and drying of the fingernails, and in certain diseases